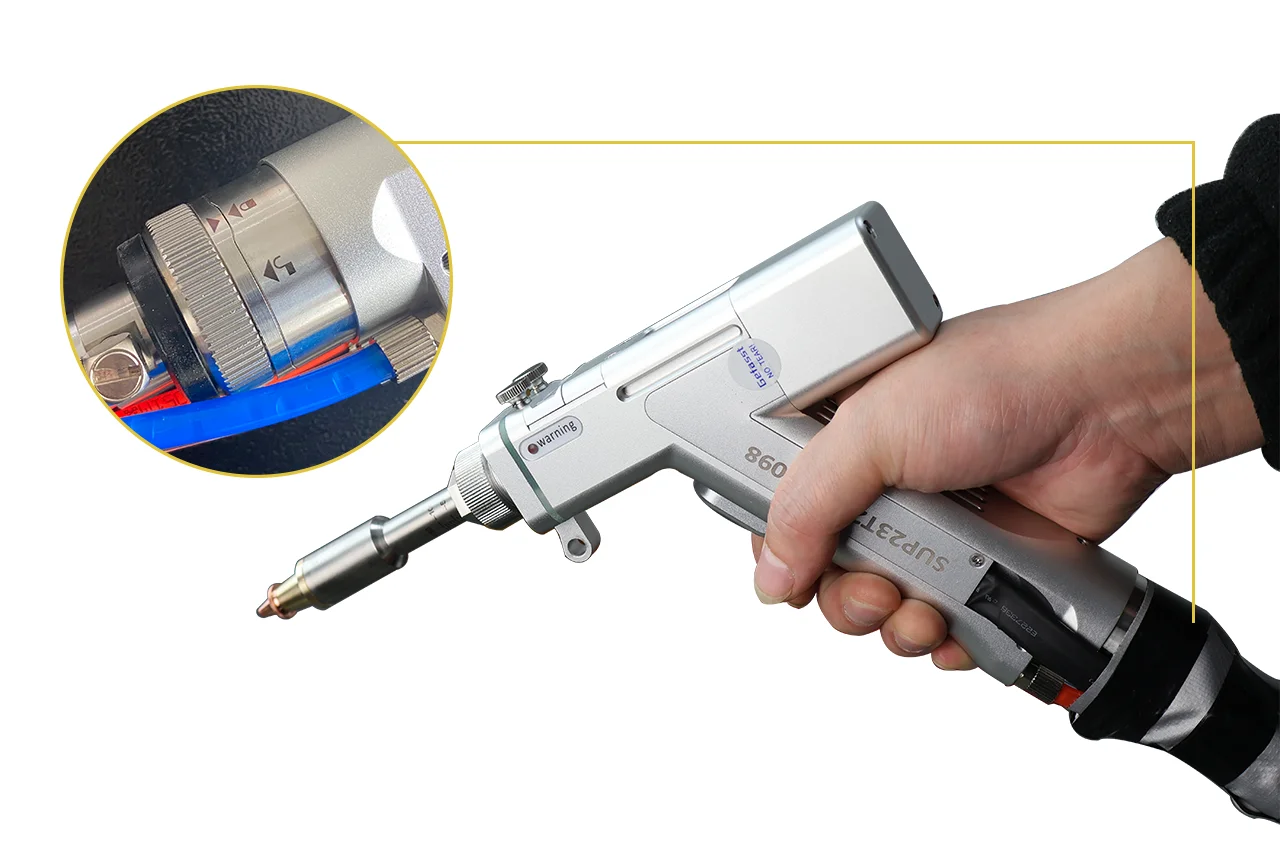
The protective lens is a critical component of your laser cleaning machine, shielding internal optics from contamination and damage. However, its lifespan isn’t indefinite, and improper replacement schedules can lead to costly downtime or even permanent equipment damage. In this blog, we’ll break down the factors influencing replacement frequency, best practices, and warning signs to help you optimize maintenance and maximize ROI.
1. Key Factors Affecting Replacement Frequency
The protective lens replacement cycle varies widely depending on operational conditions. Key factors include:
- Material Processed
- High-reflectivity metals (e.g., aluminum, copper) accelerate lens contamination due to back reflections.
- Rust, paint, or greasy materials generate more debris and fumes, increasing wear.
- Usage Intensity
- Continuous operation (>8 hours/day) shortens lens life compared to intermittent use.
- Environmental Conditions
- Dusty or humid environments cause faster contamination or oxidation.
2. General Maintenance Guidelines
A. Routine Inspection
- Daily Checks: Visually inspect the lens for scratches, stains, or coating damage before and after operation.
- Cleaning Protocol:
- Use lint-free wipes and anhydrous ethanol for gentle, unidirectional cleaning.
- Avoid abrasive materials or circular wiping to prevent micro-scratches.
B. Manufacturer Recommendations
- Under standard conditions (non-abrasive materials, moderate usage), most manufacturers suggest replacement every 40–80 operating hours.
- Always cross-reference your equipment manual for model-specific guidance.
3. Warning Signs Requiring Immediate Replacement
Don’t wait for scheduled maintenance if you notice:
- Reduced Cleaning Efficiency: Longer processing times despite unchanged laser settings.
- Abnormal Laser Output: Irregular beam patterns or energy fluctuations.
- System Alerts: Error codes related to optics (e.g., temperature warnings, power deviations).
4. Risks of Delayed Replacement
Ignoring lens wear can lead to:
- Secondary Damage: Contaminants or scratches may propagate to the focusing lens, increasing repair costs by 3–5x.
- Safety Hazards: Severely degraded lenses risk laser scattering, endangering operators.
5. Proactive Maintenance Strategies
- Track Usage Hours: Maintain a log to predict replacement timelines.
- Customize Schedules: Adjust cycles based on material types (e.g., replace every 30 hours when processing oily metals).
- Lens Quality Matters: Opt for OEM or high-grade third-party lenses to ensure compatibility and durability.
Regular protective lens replacement isn’t just a maintenance task—it’s a cost-saving strategy. By understanding your operational demands and adopting proactive measures, you can extend equipment life, ensure operator safety, and maintain peak performance.
 Triumphlaser
Triumphlaser